labral hip tear test|hip labrum physical exam test : factories The McCarthy Test is a clinical test used in the diagnosis of a hip labral tear. The shearing force-producing painful popping, clicking, or catching while performing the test indicates a possible hip labrum tear. See more Servicing and Maintenance of Priorclave Autoclaves Priorclave Laboratory Autoclaves are complex pressure systems designed and built to special regulations and as such should only .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Browse a complete Item Number list and easily reorder VERIFY™ STEAM Integrating Indicator products on Shop STERIS. Find information for VERIFY STEAM Integrating Indicator. View product specifications for this chemical .
The McCarthy Test is a clinical test used in the diagnosis of a hip labral tear. The shearing force-producing painful popping, clicking, or catching while performing the test indicates a possible hip labrum tear. See more
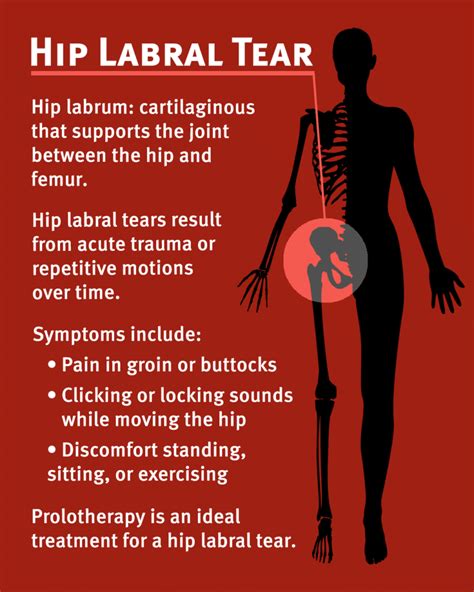
The acetabulofemoral (hip) joint is the largest and most stable joint in the human body. The acetabular labrum is a soft-tissue structure . See more
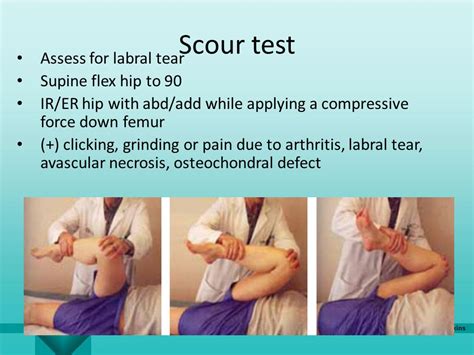
Step 1:The patient should be lying supine with their head supported and both arms rested to their side in a comfortable position. Step 2:The . See more A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. Diagnosis generally .The McCarthy Test is a clinical test used in the diagnosis of a hip labral tear. The shearing force-producing painful popping, clicking, or catching while performing the test indicates a possible hip labrum tear. A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. Diagnosis generally requires an MR arthrogram of the hip joint in question.
treatment for labral tear in hip
Imaging scans. A hip labral tear rarely occurs by itself. In most cases, other structures within the hip joint also have injuries. X-rays are excellent at visualizing bone. They can check for arthritis and for structural problems.
Diagnosing labral tears in the hip involves: Evaluating the hip joint to check for labral problems; Conducting specific hip labral tear tests to determine if the labrum may be torn or degenerated; Identifying or ruling out other hip conditions contributing to the patient’s symptomsA healthcare provider will diagnose a hip labral tear with a physical exam and some tests. They’ll examine your hip and ask you about your symptoms. Tell your provider when you first noticed pain and other symptoms, and if any activities, movements or positions make them worse.
FABER Test - The lower extremity is passively placed in a figure-of–four position, and slight pressure is applied to the medial side of the knee. (Positive in 7 of 18 cases) Resisted straight leg raise test - The patient's hip is flexed 30° with the knee in extension and a . A hip labral tear involves the ring of cartilage (labrum) that follows the outside rim of the hip joint socket. Besides cushioning the hip joint, the labrum acts like a rubber seal or gasket to help hold the ball at the top of the thighbone securely within the hip socket.
labral tear physical exam tests
A labral tear is an injury to the tissue that holds the ball and socket parts of the hip together. Torn hip labrum may cause pain, reduced range of motion in the hip and a sensation of the hip locking up. Labral tears are typically caused by overuse, traumatic injuries or abnormalities in the shape or alignment of the hip bones.
To diagnose a hip labral tear your doctor will review your medical history, conduct a physical exam, and order one or more imaging tests. As a first step toward making a diagnosis, your doctor will ask about your symptoms including when they began and which activities aggravate them.To test for an anterior labral tear, the patient lies supine, then the physical therapist (PT) performs flexion, external rotation, and full abduction of the hip, followed by extending the hip, internal rotation, and adduction.The McCarthy Test is a clinical test used in the diagnosis of a hip labral tear. The shearing force-producing painful popping, clicking, or catching while performing the test indicates a possible hip labrum tear. A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. Diagnosis generally requires an MR arthrogram of the hip joint in question.
labral special tests hip
Imaging scans. A hip labral tear rarely occurs by itself. In most cases, other structures within the hip joint also have injuries. X-rays are excellent at visualizing bone. They can check for arthritis and for structural problems.Diagnosing labral tears in the hip involves: Evaluating the hip joint to check for labral problems; Conducting specific hip labral tear tests to determine if the labrum may be torn or degenerated; Identifying or ruling out other hip conditions contributing to the patient’s symptoms
A healthcare provider will diagnose a hip labral tear with a physical exam and some tests. They’ll examine your hip and ask you about your symptoms. Tell your provider when you first noticed pain and other symptoms, and if any activities, movements or positions make them worse.FABER Test - The lower extremity is passively placed in a figure-of–four position, and slight pressure is applied to the medial side of the knee. (Positive in 7 of 18 cases) Resisted straight leg raise test - The patient's hip is flexed 30° with the knee in extension and a .
A hip labral tear involves the ring of cartilage (labrum) that follows the outside rim of the hip joint socket. Besides cushioning the hip joint, the labrum acts like a rubber seal or gasket to help hold the ball at the top of the thighbone securely within the hip socket.
A labral tear is an injury to the tissue that holds the ball and socket parts of the hip together. Torn hip labrum may cause pain, reduced range of motion in the hip and a sensation of the hip locking up. Labral tears are typically caused by overuse, traumatic injuries or abnormalities in the shape or alignment of the hip bones.To diagnose a hip labral tear your doctor will review your medical history, conduct a physical exam, and order one or more imaging tests. As a first step toward making a diagnosis, your doctor will ask about your symptoms including when they began and which activities aggravate them.
how can one heal a hip labral tear
hip labrum tear recovery without surgery
hip labrum physical exam test
If everything seems fine with the power, the issue could be with the door. Autoclaves have safety features that prevent operation if the door isn’t properly sealed. Check the door seal for any damage and ensure it’s closed .What to do when the autoclave door will not open.
labral hip tear test|hip labrum physical exam test